Objective setting in rehabilitation
Objective setting is a crucial component of rehabilitation, as it breaks down overarching goals into actionable, manageable steps that guide progress and facilitate achievement. By setting clear objectives, patients and clinicians can focus on specific tasks that contribute to the broader rehabilitation goal, making the journey more structured and achievable.
Objectives provide a clear roadmap, ensuring that efforts remain targeted and aligned with the patient’s needs. They help in setting expectations, tracking progress, and maintaining motivation throughout the rehabilitation process. Well-defined objectives empower patients to take ownership of their recovery while allowing clinicians to provide targeted support.
Within an interdisciplinary team (IDT), objectives play an essential role by allowing various professionals to collaborate effectively while addressing different aspects of the same goal. Each team member can work on their specific objective, utilising their expertise while ensuring their contributions align with the shared goal.
This coordinated approach enhances efficiency and cohesion, ensuring that all facets of the patient's needs are comprehensively addressed. It promotes a holistic rehabilitation process where medical, therapeutic, and social aspects are considered in unison, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
SMART objectives
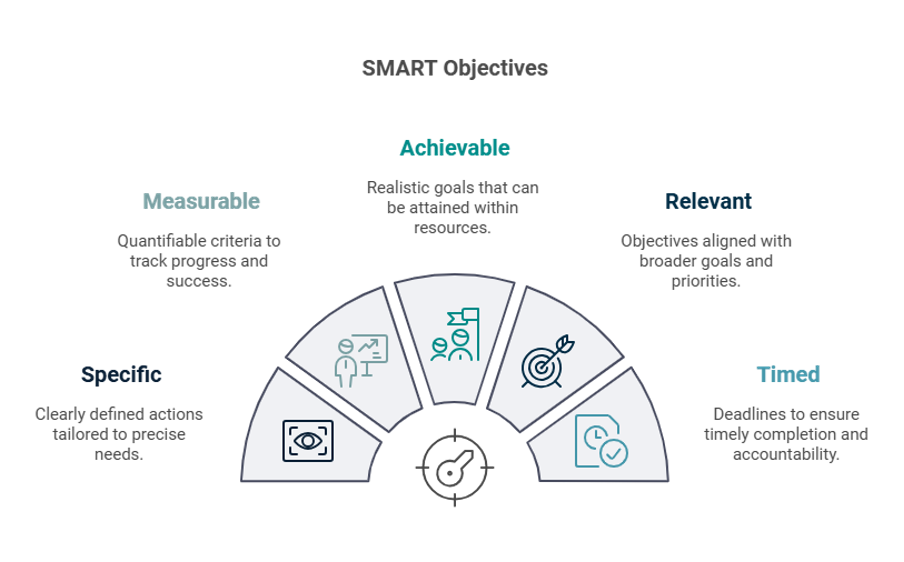
Kompass utilises the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Timed) objective structure to help break down rehabilitation goals into actionable steps. Recognised widely in rehabilitation literature, SMART objectives provide an effective framework for structuring tasks that contribute to achieving broader goals.
Unlike overarching goals, which are shared by the entire team, SMART objectives focus on specific, detailed actions assigned to individual clinicians or team members. This targeted approach ensures accountability for short-term contributions while maintaining alignment with the overall rehabilitation plan.
Breaking objectives into clear, structured sections enhances their effectiveness by making them measurable, time-bound, and attainable. It also increases the likelihood of success by ensuring that each step is well-defined and achievable within the given timeframe.
By implementing SMART objectives, Kompass ensures that rehabilitation efforts remain organised and outcome-driven, allowing teams to track progress efficiently and adjust strategies as needed. This structured method keeps the focus on both short-term tasks and long-term goals, fostering a more coordinated and effective rehabilitation process.
Using the SMART framework
When creating objectives, use the following prompts for each component of the SMART framework:
Summary
Provide a clear and concise title or overview that captures the essence of the objective.
Ensure the summary aligns with the overall rehabilitation goals and provides context for all staff members involved in the process.
Specific
Clearly define the therapeutic interventions, including the dosage (e.g., number of sessions).
Outline the treatment plan, detailing session content and progression steps.
Specify the exact actions needed to accomplish the objective.
Measurable
Establish clear methods for tracking progress, such as self-report questionnaires, assessments, observations, or feedback.
Identify key indicators and variables to monitor progress effectively.
Achievable
Evaluate whether the necessary resources, skills, and support systems are available.
Recognise potential challenges and opportunities, considering relevant ICF assessment insights if applicable.
Relevant
Ensure the objective aligns with the patient’s overall goals and daily life activities.
Incorporate the patient’s values, preferences, and priorities to enhance engagement.
Timed
Set a specific timeframe and target date for achieving the objective, ensuring a clear and realistic deadline.
Ready to streamline goal-setting?
Contact usGetting started with SMART objectives
If you're new to the SMART framework, begin by:
Setting broad goals using the GAS framework:
The Goal Attainment Scaling (GAS) framework helps set personalised, broad goals by defining baseline levels and measuring progress through incremental targets. It ensures goals are patient-centered, adaptable, and aligned with their long-term aspirations. GAS allows flexibility in tracking progress, accommodating both improvements and setbacks to provide a comprehensive rehabilitation roadmap.
Breaking down each goal into smaller, actionable steps using the SMART framework:
The SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Timed) breaks broad goals into clear, actionable steps. It ensures objectives are well-defined, trackable, and realistic within a set timeframe. SMART objectives provide a structured approach that enhances focus, accountability, and the ability to measure success effectively.
Focusing on the steps needed for the patient to achieve their goals:
Achieving goals requires focusing on specific steps that align with the patient’s abilities and needs. Providing clear guidance, regular progress tracking, and adjustments helps maintain motivation and ensures steady progress. Engaging patients in their rehabilitation journey fosters ownership and commitment to their goals.
Tips to Start:
Focus on your contribution to patient progress.
Assess how your input can directly support the patient's rehabilitation journey and contribute to meaningful improvements.
Define discipline-specific actions.
Identify practical steps within your area of expertise that can be implemented to support the broader rehabilitation goals.
Plan objectives by working backward.
Start with the end goal in mind and break it down into smaller, manageable steps to create a clear and achievable pathway.
Steps to Effective Rehabilitation
Objective Setting
Translating goals into actionable steps for progress.
Goal Setting
Creating structured, patient-centered goals to guide rehabilitation.
Identify Problems
Highlighting key areas requiring intervention based on the assessment.
Functional Assessment
Establishing a comprehensive understanding of the patient's abilities and limitations.
Within Kompass, you can link SMART objectives to specific goals or create standalone objectives as necessary. This flexibility allows for comprehensive and effective rehabilitation planning by ensuring that each objective aligns with the patient's overall treatment plan. Linking objectives to goals helps track progress more efficiently, fosters interdisciplinary collaboration, and ensures consistency across different areas of care. Additionally, standalone objectives provide the flexibility to address immediate priorities or evolving patient needs, enabling a more personalised and adaptive approach to rehabilitation.